3 Types of Edge Computing and When To Use Them

New types of end-user experiences powered by emerging technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) need compute power that’s closer to where a device or data source exists—at the network’s edge. But the edge isn’t a single location: it can be on-premises, at the cloud edge or even in the public cloud. In this post, we explore how these edge computing models can equip your business to power next-gen applications from virtually anywhere.
Closer than the cloud
Edge computing is a new way to deliver data and applications closer to where the data is generated. It’s like bringing millions of smaller cloud environments closer to the billions of devices that make up the IoT.
Unlike cloud computing—which consolidates data processing in large, centralized data centers that may be hundreds of miles from where data is collected—edge computing allows enterprises to place compute and storage where interactions between people and devices occur. This enables companies to deliver more satisfying end-user experiences, support latency-sensitive use cases and innovate faster with technologies such as AI and machine learning.
Added benefits include greater reliability, potentially stronger security and lower costs, giving companies a powerful incentive to move some of their processing to the edge.
But edge computing isn’t a one-dimensional approach. If you’re thinking of moving your business to the edge, you should understand the various deployment options and how they align with your business and IT goals.
It’s all about location
The idea behind edge computing is straightforward: if you can’t get your data closer to your data center, you move your data center closer to your data. You can do that by creating a distributed environment in which your apps live closer to end users and devices. That environment comprises three locations: the premises edge, the edge cloud and the public cloud.
Let’s take a closer look at these three types of edge and their unique features.
Premises edge
As the name suggests, the premises edge is dedicated compute and storage that resides on customer premises—for example, a corporate office, sports stadium, retail store or manufacturing plant.
On-premises compute devices serve as edge gateways that can deliver network routing, security services and data filtering, and even host applications. These edge devices can take many forms, such as an IoT sensor, laptop computer, security camera or a robot on an assembly line.
Because devices on the premises edge have a much shorter, direct path to the edge cloud, latency is extremely low—typically less than 1 millisecond. Companies often choose this approach when they need ultra-low latency for mission-critical applications.
Premises edge computing can be costlier than other types of edge computing, since it requires separate setup and configuration for each location and device, along with staff to manage it. However, since the customer controls the devices, hardware and software, this approach is considered highly reliable and secure.
When to use it
Premises edge solutions support use cases such as:
•Detecting anomalies in manufacturing
•Managing real-time process control
•Delivering real-time VR/AR experiences
•Providing tactile internet applications
•Running AI optical inspection
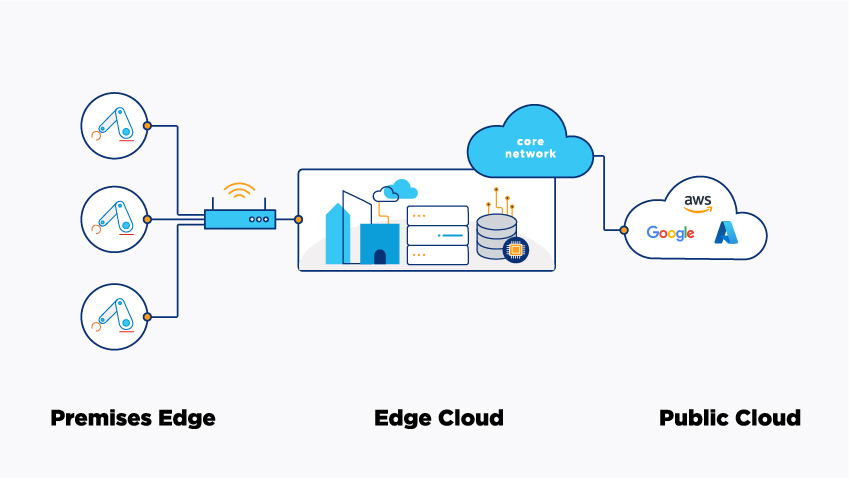
Figure 1: How premises edge, edge cloud and public cloud work together to create a distributed IT infrastructure
Edge cloud
The edge cloud is a unique combination of local compute and storage with high-capacity fiber, built-in security and unified orchestration that offers the best of both worlds. Also called the metro edge or market edge, it leverages cloud and edge resources to form a distributed network of data storage and transfer from edge applications.
Edge cloud data centers are home to compute and storage services such as bare metal, network storage and virtual machines. Located in low-latency (typically 5ms or better) edge nodes, the edge cloud provides direct connections to public cloud service providers.
When to use it
The edge cloud can provide the speed and performance you need to handle data-heavy apps and compute-intense edge workloads such as:
•Real-time promotions
•Digital signage
•Inventory management
•Predictive maintenance
Public cloud
The public cloud is an IT model where on-demand computing services and infrastructure are managed by a third-party provider and shared with multiple organizations using the public internet.
AWS, Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure are examples of public cloud providers, where customers share the same hardware, storage and network devices with other organizations (or tenants), accessing services and managing resources via a web portal.
The public cloud typically delivers 30-80ms of latency, making it suitable for processing non-critical workloads. Many factors can affect the speed at which data travels to the cloud, such as the number of network hops on the way to the target server. Because cloud service data centers may be physically located anywhere in the world, latency can vary greatly from facility to facility.
When to use it
Ideal public cloud use cases include:
•Omni-channel pricing and merchandising
•Customer lifecycle management and customer relationship management (CRM)
•Big data or AI-enabled product design and testing
Which type of edge is right for you?
If you’re wondering which edge is right for you, the answer depends on your applications and use cases. If you only think about edge as a single location, you won’t have everything you need to take advantage of new technologies and deliver differentiated customer experiences in an evolving marketplace.
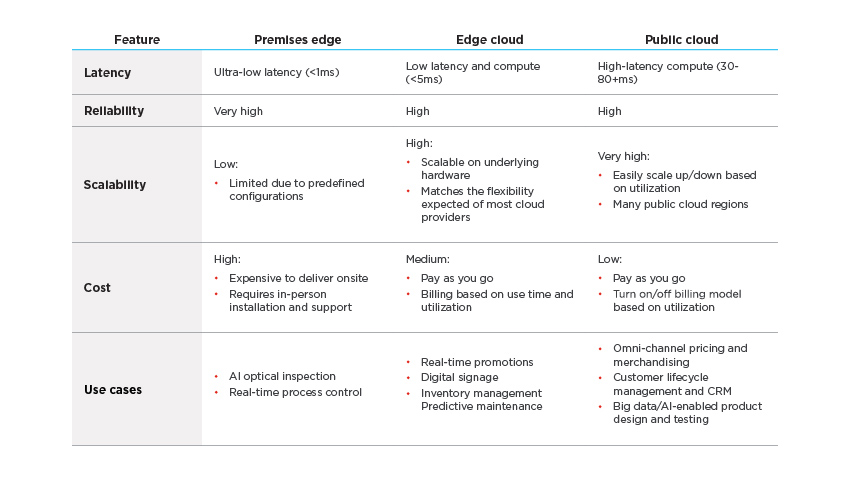
Here’s a side-by-comparison of edge capabilities to help you see which environments can best support the apps and workloads powering your business.
Find your edge with Lumen
When you’re ready to start moving your resources to the edge, we can help you manage your multiple cloud and edge locations efficiently and cost-effectively.
Our edge-first architecture is built to deliver optimal latency, performance and reliability whether your applications live on the premises edge, edge cloud or public cloud. By integrating low-latency edge compute, cloud, storage, networking, security and orchestration, we can deliver the resources you require across a continuum so you can pick the right place depending on your application needs.
Through our combination of ~160,000+ on-net fiber locations, dense fiber connections used by private cloud providers and our network of low-latency edge nodes designed to deliver <5ms or better latency to 97% of U.S. businesses, we can dramatically shorten the distance your data needs to travel. So you can easily deploy next-gen technologies that deliver outstanding experiences from Austin to Atlanta to wherever you do business.
This content is provided for informational purposes only and may require additional research and substantiation by the end user. In addition, the information is provided “as is” without any warranty or condition of any kind, either express or implied. Use of this information is at the end user’s own risk. Lumen does not warrant that the information will meet the end user’s requirements or that the implementation or usage of this information will result in the desired outcome of the end user. This document represents Lumen’s products and offerings as of the date of issue. Services not available everywhere. Business customers only. Lumen may change or cancel products and services or substitute similar products and services at its sole discretion without notice. ©2023 Lumen Technologies. All Rights Reserved.
1IDC Research, Edge Computing Solutions Powering the Fourth Industrial Revolution, January 2021.






